
WIRELESS CHARGING IN THE NEWS

Core definition: The cage elevator is a core vertical transportation equipment in the mining industry (mainly underground mines such as coal mines and metal mines). Essentially, it is a large lift elevator pulled by steel wire ropes and running along vertical or inclined tracks. But it is different from ordinary elevators:


As the backbone force of intelligent logistics, the continuous operation capacity of AGV is a key link that determines the efficiency of the entire system. However, the traditional contact charging mode has many constraints and is becoming a "stumbling block" on the road to the wide application of AGVs.


Advanced wireless charging delivers unparalleled freedom: high misalignment tolerance allows robots to charge naturally (standing, lying, tilted, crouched). Eliminates complex positioning, simplifies deployment, and boosts operational robustness. The key to seamless “work-charge” cycles in any environment, enabling true 24/7 autonomy. Power, unbounded.
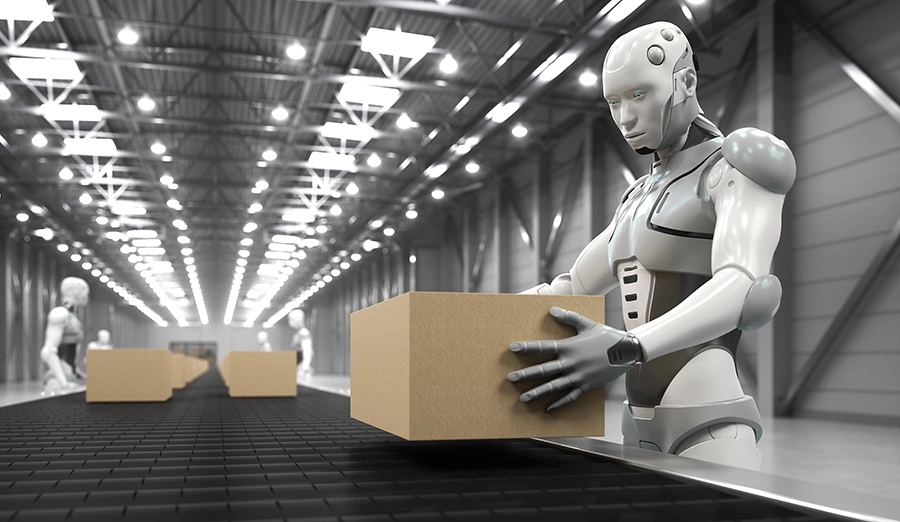


Facing critical weight/space constraints in bionic robots, wireless charging provides a "stealth" solution: ultra-miniaturized receivers boast high power density, low heat loss, and superior integration, minimizing impact on balance and freeing resources for core functions – empowering unparalleled performance. Gram mastery, power unleashed.

Wireless charging eliminates the tether trap of embodied robots. It removes motion interference, enhances freedom and flexibility, supports critical needs like charging after falls, unlocking their true bionic potential. Cut the cord, unleash the motion.


Endorsed by national research institutions and holding comprehensive patents, the technology proved its mettle with leading brands: users in rainy regions report transformative reliability improvements. WIRELESSPT now invites collaboration on tailored charging solutions with exclusive benefits for early partners, empowering Chinese robotics to overcome their final energy barrier.


Deep supply chain integration catalyzes further gains, where breakthroughs in domestic component manufacturing enhance performance while optimizing costs. With steadily growing international certification coverage, Chinese brands now deliver region-specific solutions to emerging markets.
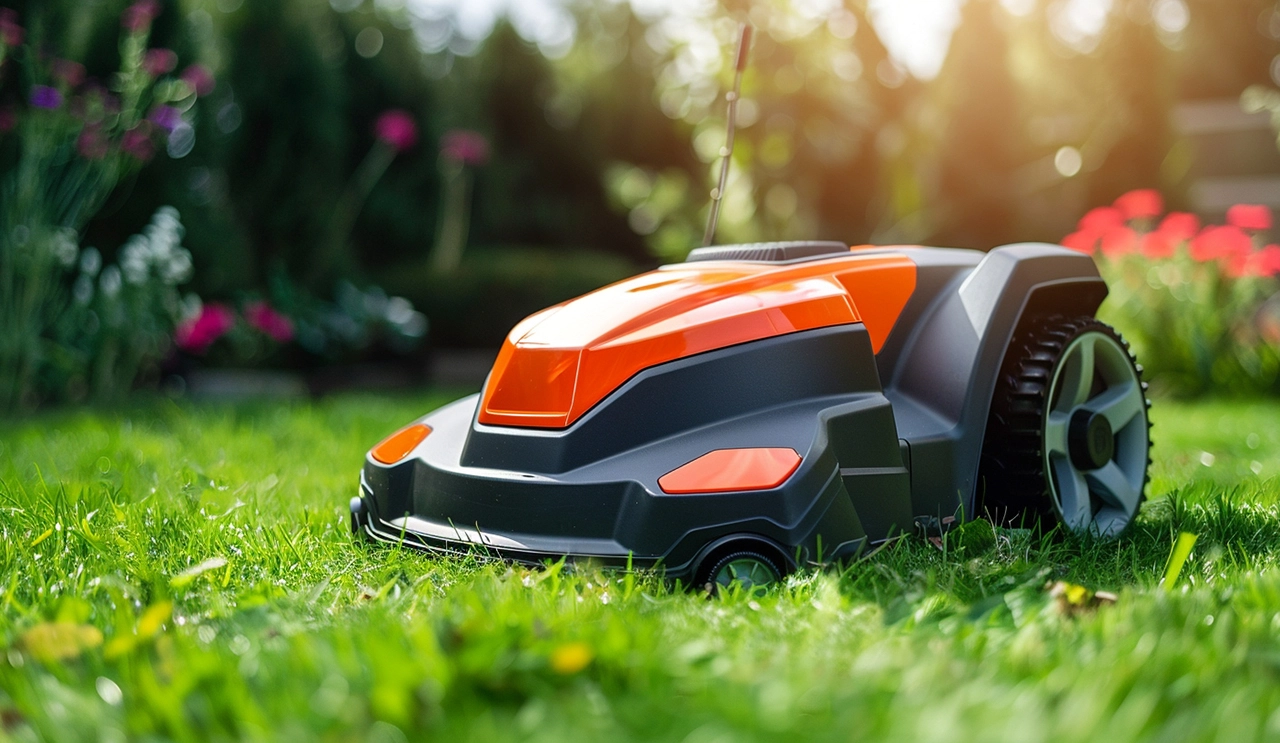


The quiet hum of Chinese-made robotic mowers in European gardens signals their growing global popularity. Tightening environmental regulations and rising labor costs have positioned smart navigation-enabled Chinese products as preferred solutions. Pioneers like Greenworks employ advanced positioning systems enabling autonomous pathfinding in complex landscapes, with obstacle avoidance capabilities earning wide acclaim.
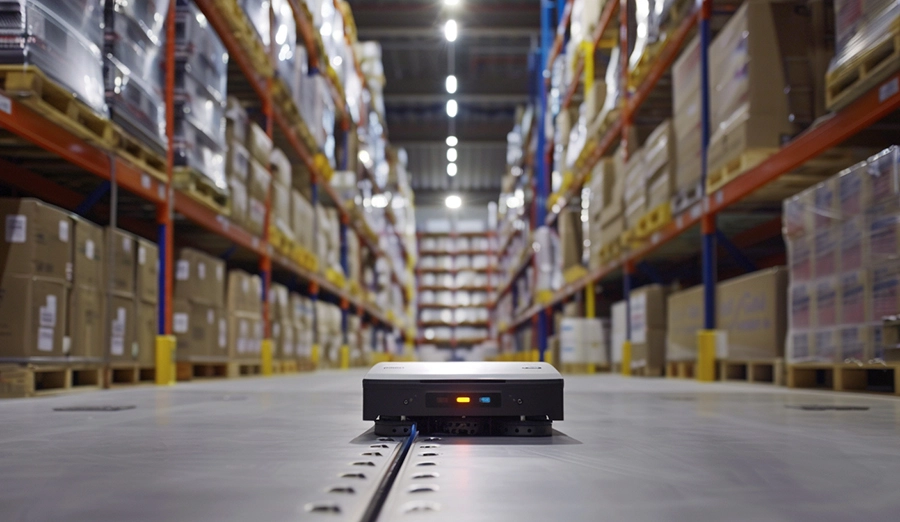


At the neural endpoints of a smart factory, every autonomous mobile robot (AMR) acts as a cell powering the production pulse. As these cells require "energy replenishment," wireless charging systems are quietly transforming from mere power suppliers into the central decisionmaking hub of factory energy – they don't just charge; they conduct a symphony of data.

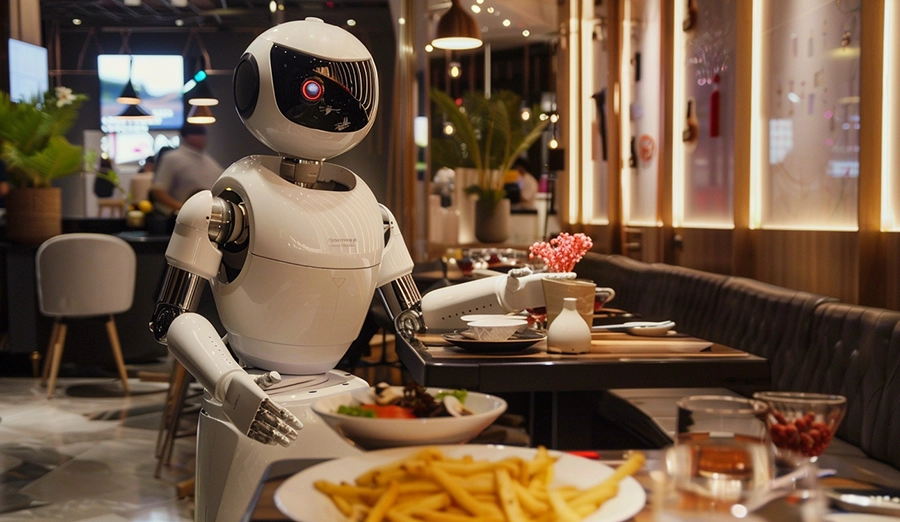
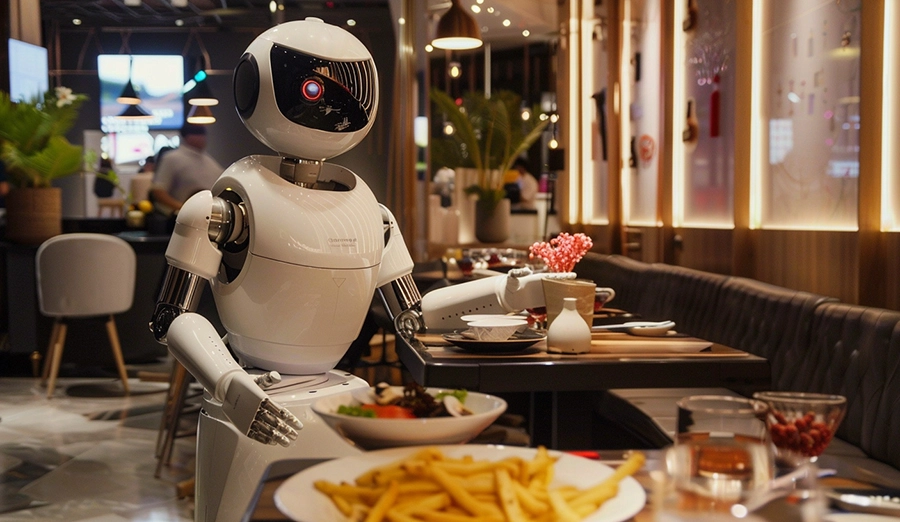
Wireless charging enables humanoid robots to replenish energy seamlessly during service breaks, eliminating the sense of interruption and mechanical movements. 24/7 natural services are provided in scenarios such as hotels and exhibition halls, enhancing professionalism and user trust, and creating differentiated competitiveness for operators and robot companies.


Wireless charging invisibly embedded in counters, millwork, or carpets eliminates cord clutter and tripping hazards. It elevates aesthetics and safety in premium spaces, enabling elegant, seamless power replenishment for humanoid robots while preserving design integrity.


Wireless charging isn’t just power transfer—it’s the keystone of autonomous manufacturing. By liberating humans from manual tasks, we redirect talent to highvalue innovation. When we bid farewell to plugs, factory lights stay off not to save energy, but because machines have learned to power themselves.
